Google Chrome is the most popular browser in the US, and most likely around the world. People love it for its speed, plugins, and minimalist design. Managing Google Chrome in a corporate environment is a bit challenging though, especially if you manage your user’s browser settings through a network policy like a domain controller GPO. If you are reading this article because you want to change the home page, add URLs to “trusted” sites, prevent Google Chrome from auto updating itself on people’s computers etc. then continue reading on because I will guide you step by step on how you can do that using a group policy in a Windows domain controller.
Table of Contents
Downloading the policy template
From your domain controller ( or any other computer if you don’t browse the Internet on your domain controller ) download these policy templates https://dl.google.com/dl/edgedl/chrome/policy/policy_templates.zip unzip the file, and take note of the path.
Importing the template to your GPO management console
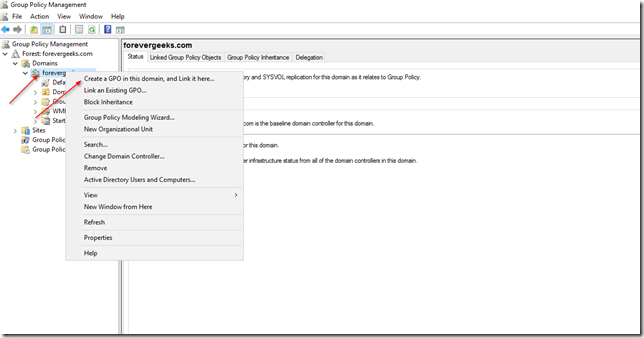
Login to your domain controller, and open your Group Policy Management console. Right-click your network domain and choose “Create a GPO in this domain, and link it here”
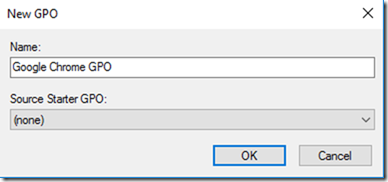
Name the GPO.
Click Ok.
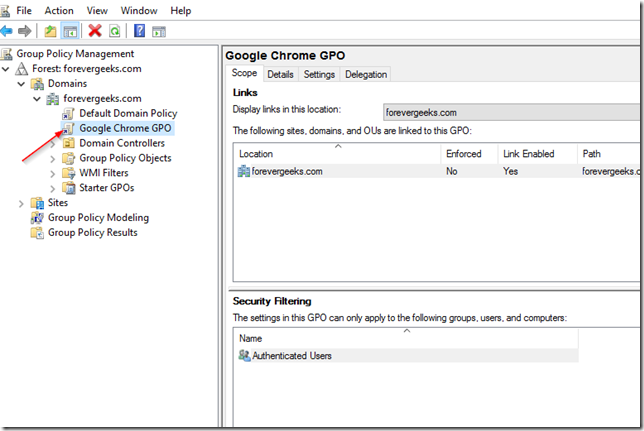
Your Google Chrome GPO should be listed on your console now:
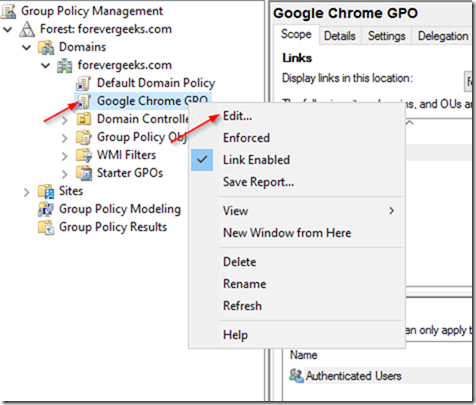
Right-click on your policy and choose Edit:
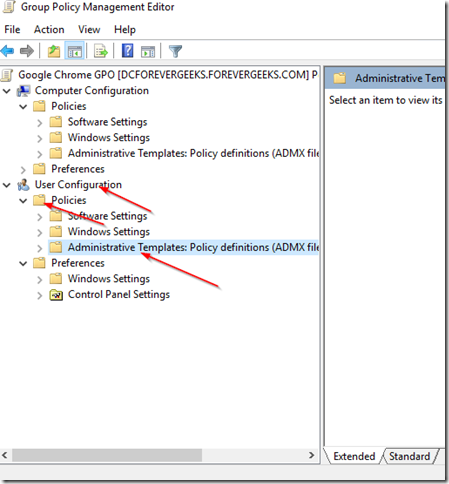
Then go to this location: User configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates:
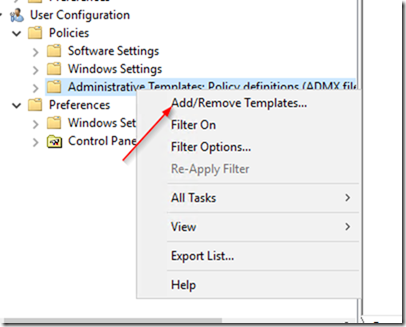
Right-click the administrative templates and click on Add/Remove Templates…
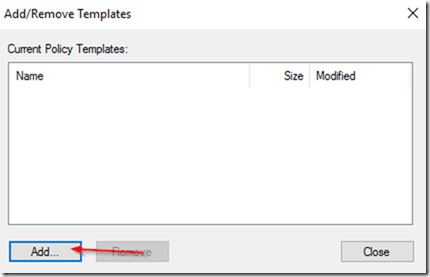
Then click on Add:
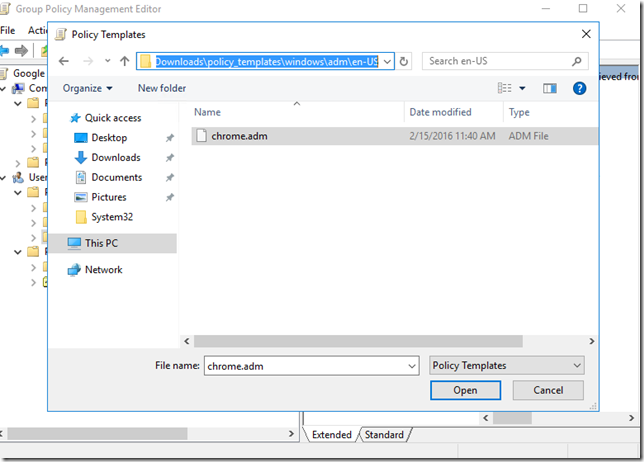
Navigate to the policy template you downloaded earlier, and go to this path “policy_templateswindowsadmen-US” ( choose any other language if you need to ) and add the Chrome.adm file:
click on Open and then Close.
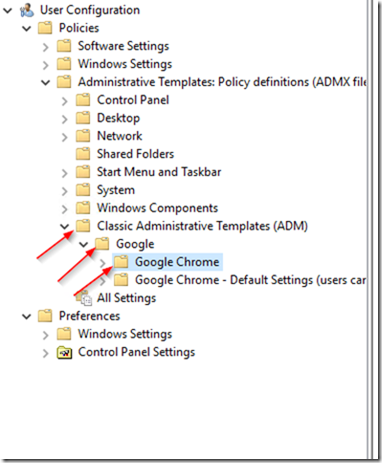
Your Google Chrome Policy should be listed under “Classic Administrative Templates ( ADM > Google > Google Chrome:
Setting the Home Page
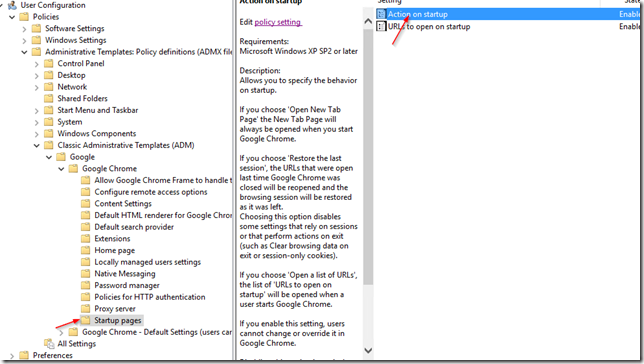
To set your Intranet or any other URL as the home page in Google Chrome using a GPO open your Group Policy Management console and go to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Classic Administrative Templates (ADM) > Google > Google Chrome. There are two settings we need to enabled. Startup Pages ( the pages that open up when users open Google Chrome ) and the Home Page which is where we set the home page URL. so go to Startup pages and double click the Action on startup setting:
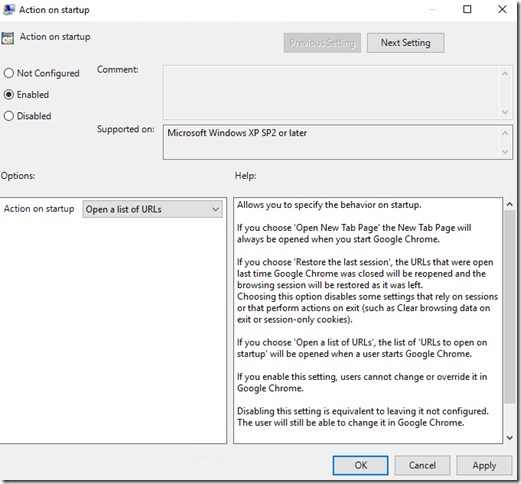
Click on Enabled then on the “Action on startup” selection box, choose Open a list of URLs:
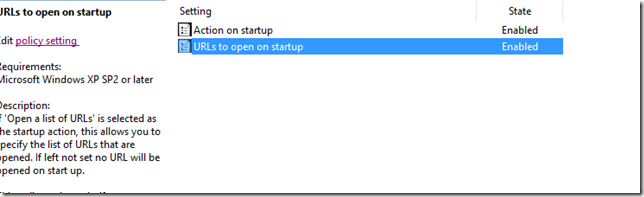
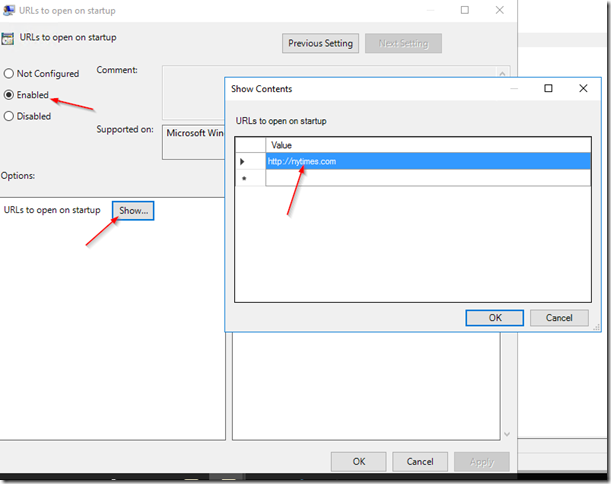
Click OK. now click on URLs to open at startup setting:
Click Enabled and then click on Show:
Enter the URL that you want to set as Home Page, and then click on OK.
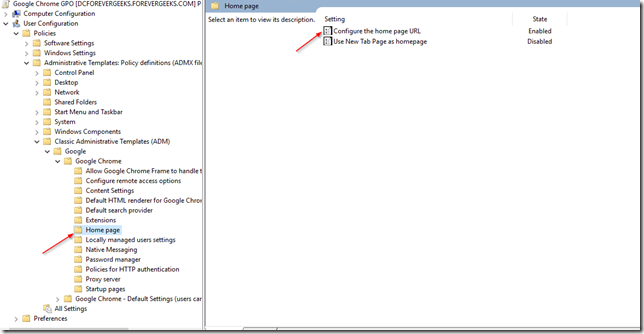
Now click on the Home Page folder:
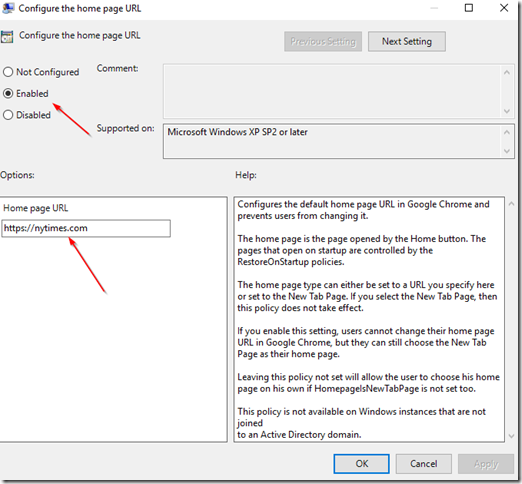
Open the Configure the Home page URL setting, click on Enabled and enter the Home Page URL:
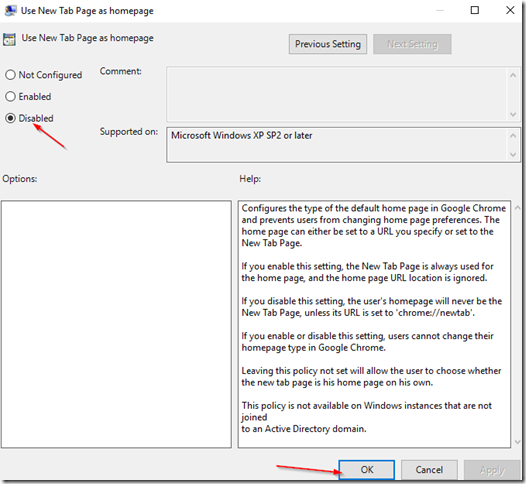
Click on Apply and then click on Next Setting. click on Disabled on the next screen, and then click Apply and then OK.
Add URLs to trusted Sites
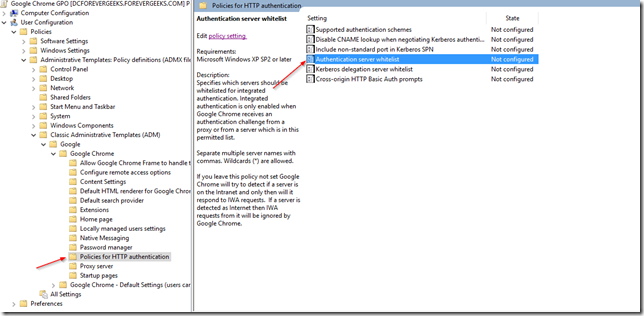
In Google Chrome there is no such thing as trusted sites, but you can accomplish almost the same thing using the Authentication server whitelist setting. What does this do? this is helpful when you have an Windows single sign-on Intranet site, and you don’t want your users to be prompted for credentials to login. it basically enables Kerberos seamless authentication. to enable it go to Policies HTTP Authentication and the open the Authentication server whitelist setting:
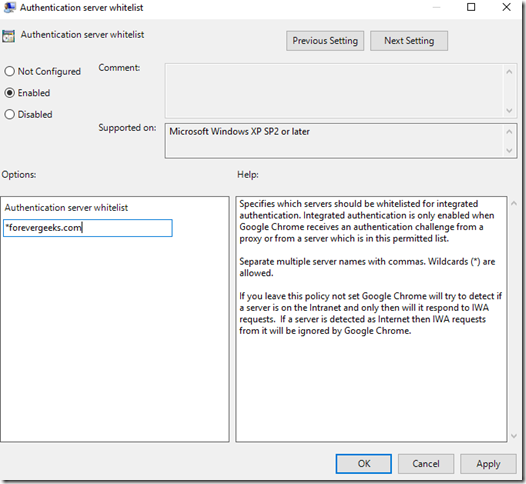
On the next screen click on Enabled then add the URLs you want to whitelist:
Click OK.
Testing the GPO
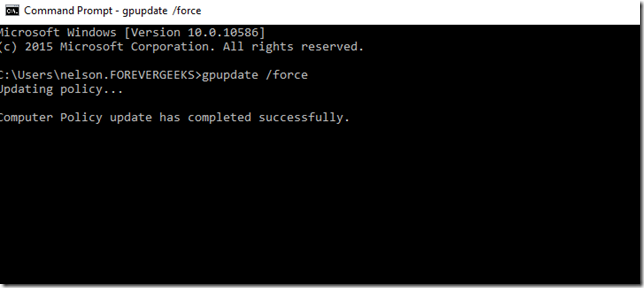
Now the moment of truth. login to any computer on your network, and open the CMD command prompt, and type gpupdate /force :
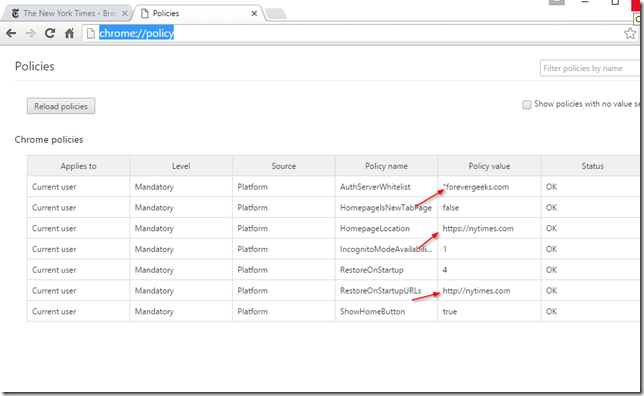
Now open Google Chrome and see if the GPO Home Page settings are applied. In your browser type-in chrome://policy to see if the Authentication server whitelist setting was applied:
Great!!
Conclusion
Setting GPO policies in Google Chrome is a little bit more involved than setting policies in other browsers like IE and Firefox. I hope you found this step by step guide helpful. if you have any question please use the comment section below.
Was this article helpful?
Your feedback helps us improve our content.
115 people found this helpful!