The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Framework is a comprehensive cybersecurity guide that helps organizations manage and reduce cybersecurity risks. The framework is comprised of three main components: the Core, the Implementation Tiers, and the Profiles. In this article, we will focus on the Core component, which serves as the foundation for an organization’s cybersecurity risk management strategy. We will explore its structure, functions, and benefits for organizations looking to improve their cybersecurity posture.
If you want a quick overview of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework you can go here
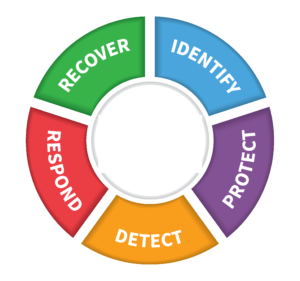
Table of Contents
I. The NIST Framework Core Component: An Overview
The NIST Framework Core component is a set of cybersecurity activities and outcomes designed to provide a high-level, strategic view of an organization’s cybersecurity risk management. It is organized into five primary functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Each function consists of categories and subcategories that offer a more granular understanding of the specific actions needed for effective cybersecurity management. The Core enables organizations to align their cybersecurity measures with their business requirements, risk tolerance, and available resources.
II. The Five Functions of the NIST Framework Core Component
1. Identify
The Identify function helps organizations develop an understanding of their systems, assets, data, and overall risk exposure. This function provides a foundation for making informed decisions about cybersecurity priorities and resource allocation.
Key Categories and Subcategories:
– Asset Management
– Inventory and classification of physical and software assets
– Management of data and information
– Business Environment
– Understanding the organization’s role in the supply chain
– Identification of critical services and their dependencies
– Risk Assessment
– Assessment of risks to organizational operations
– Identification of vulnerabilities, threats, and likelihoods
– Risk Management Strategy
– Establishment of risk management processes and priorities
– Integration of risk management into organizational culture
2. Protect
The Protect function focuses on implementing safeguards to ensure the delivery of critical infrastructure services. This function helps organizations limit or contain the impact of potential cybersecurity events.
Key Categories and Subcategories:
– Access Control
– Management of user access and permissions
– Implementation of secure authentication mechanisms
– Awareness and Training
– Development of a cybersecurity awareness program
– Training for employees, partners, and stakeholders
– Data Security
– Secure handling, storage, and transmission of data
– Implementation of data loss prevention measures
– Information Protection Processes and Procedures
– Development and maintenance of security policies and procedures
– Regular review and update of security documentation
– Protective Technology
– Implementation of security solutions and tools
– Regular patching and updating of software
3. Detect
The Detect function enables organizations to identify the occurrence of a cybersecurity event in a timely manner. Rapid detection is crucial for minimizing the potential impact of a cyber attack.
Key Categories and Subcategories:
– Anomalies and Events
– Identification of unusual activity or security events
– Analysis of network traffic patterns
– Security Continuous Monitoring
– Monitoring of assets and networks for security events
– Regular vulnerability scanning and assessments
– Detection Processes
– Establishment of detection procedures and protocols
– Integration of threat intelligence into detection efforts
4. Respond
The Respond function outlines the appropriate actions to take once a cybersecurity event has been detected. This function ensures that organizations can effectively contain and mitigate the effects of an incident.
Key Categories and Subcategories:
– Response Planning
– Development of an incident response plan
– Regular review and updating of the response plan
– Communications
– Coordination with internal and external stakeholders during an incident
– Disclosure of security events to affected parties
– Analysis
– Identification of the nature and scope of a cybersecurity event
– Evaluation of the effectiveness of existing protections
– Mitigation
– Containment and removal of threats
– Implementation of corrective actions to prevent recurrence
– Improvements
– Lessons learned from incidents to improve response processes
– Updating response plans and strategies based on new information
5. Recover
The Recover function outlines how organizations can restore their services and operations after a cybersecurity event. This function helps organizations return to normal operations while minimizing the impact on business continuity.
Key Categories and Subcategories:
– Recovery Planning
– Development of a comprehensive recovery plan
– Regular review and updating of the recovery plan
– Improvements
– Incorporation of lessons learned from incidents into recovery processes
– Updating of recovery plans based on new information
– Communications
– Coordination with internal and external stakeholders during recovery efforts
– Sharing of recovery progress and status updates with affected parties
III. Benefits of using the NIST Framework
The NIST Framework offers numerous benefits to organizations looking to improve their cybersecurity posture:
– Flexibility: The NIST framework can be tailored to an organization’s unique needs and risk tolerance, ensuring that the framework remains relevant and scalable.
– Comprehensive Approach: The five functions of the Core provide a holistic view of an organization’s cybersecurity management, covering all aspects from risk identification to recovery.
– Common Language: The Core facilitates communication and collaboration between organizations, promoting a more unified approach to tackling cybersecurity challenges.
– Continuous Improvement: The iterative nature of the Core encourages organizations to regularly assess and update their cybersecurity measures in response to a rapidly changing threat landscape.
IV. Conclusion
The NIST Framework serves as the foundation for an organization’s cybersecurity risk management efforts. By adopting the Core’s five functions and their underlying categories and subcategories, organizations can build a comprehensive and resilient cybersecurity posture. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the NIST Framework offers a robust and flexible solution that can be tailored to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities, ensuring the long-term success and security of businesses in the digital age.
Was this article helpful?
Your feedback helps us improve our content.
1 people found this helpful!

